Introduction
macchina.io EDGE is an open source software toolkit for quickly building embedded applications for the Internet of Things that run on Linux-based devices like the Raspberry Pi, Beaglebone or similar. It implements a web-enabled, modular and extensible JavaScript and C++ runtime environment and provides readily available, easy to use building blocks that allow your application to talk to various sensors and devices, as well as cloud services.
macchina.io EDGE combines the power of JavaScript for rapid application development with the power and performance of native C++ code. macchina.io EDGE is based on the POCO C++ Libraries and the V8 JavaScript engine. A unique bridging system and a code generator make it easy to consume C++ services from JavaScript, without the need to manually write glue code.
Overview
macchina.io EDGE has been built in a very modular and extensible way. Figure 1 shows the system architecture of macchina.io EDGE, which is also reflected in the source code layout.
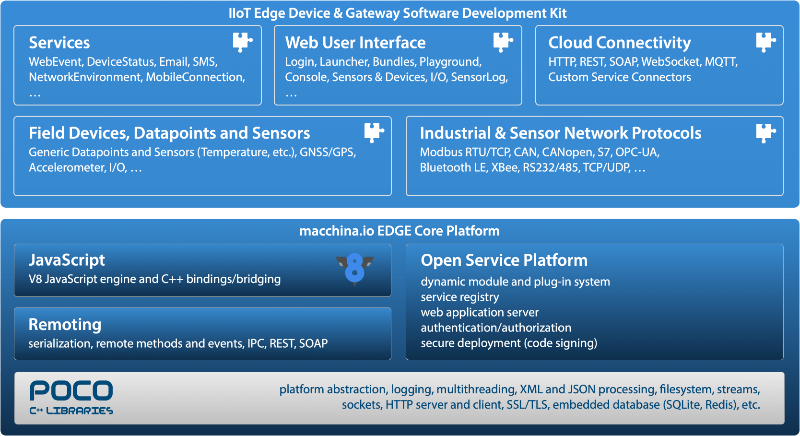
macchina.io EDGE is mostly implemented in C++. Although JavaScript plays a big role in macchina.io EDGE as the primary language for application development, it is not used much in the implementation of macchina.io EDGE itself, except for some parts of the web user interface.
Platform
The foundation for macchina.io EDGE is what we call the "Platform". It consists of the POCO C++ Libraries, the Remoting framework, the Open Service Platform (OSP) and the JavaScript environment, based on the V8 JavaScript engine. The platform is very generic and not specific to macchina.io EDGE. Although it has been optimized for use in Embedded Linux systems, it can be used to build other kind of (server) applications as well.
POCO C++ Libraries
The POCO C++ Libraries are modern, powerful open source C++ class libraries and frameworks for building network- and internet-based applications that run on desktop, server, mobile and embedded systems. They provide essential features such as platform abstraction, multithreading, XML and JSON processing, filesystem access, logging, stream, datagram and multicast sockets, HTTP server and client, SSL/TLS, etc. Virtually everything implemented in macchina.io EDGE (except some integrated third-party open source projects) is based on the POCO C++ Libraries.
Open Service Platform
The Open Service Platform (OSP) enables the creation, deployment and management of dynamically extensible, modular applications, based on a powerful plug-in and services model. Applications built with OSP can be extended, upgraded and managed even when deployed in the field.
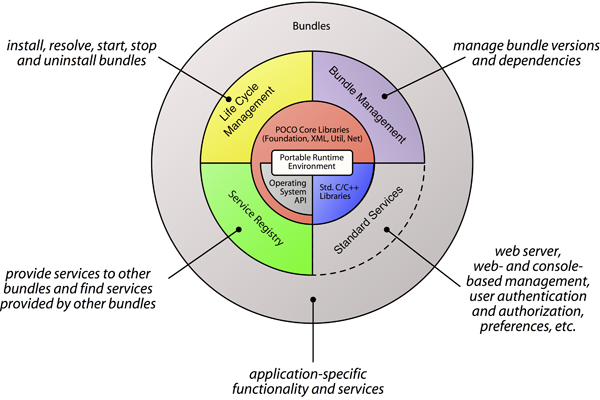
At the core of OSP lies a powerful software component (plug-in) and services model based on the concept of bundles. A bundle is a deployable entity, consisting of both executable code (shared libraries or JavaScript) and the required configuration, data and resource files (e.g., HTML documents, images, stylesheets required for a web site). Bundles extend the functionality of an application by providing certain services. A central Service Registry allows bundles to discover the services provided by other bundles. Bundles can be installed, upgraded, started, stopped or removed from an application (programmatically, or using a web- or console based administration utility) without the need to terminate and restart the application.
The Open Service Platform has been developed by Applied Informatics. It was first released under a commercial license. For macchina.io EDGE, the core of OSP has been released under an open source license. The full version of OSP (including features such as a command shell framework, improved user authentication and authorization including LDAP support, cryptographically signed bundles, etc.) is available from Applied Informatics under a commercial license.
Remoting
Remoting is a distributed objects and web services framework for C++. With Remoting, building distributed applications, implementing high-level object-based inter-process communication (IPC)/remote method invocation (RMI) or web services based on the Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) and the Web Service Definition Language (WSDL) becomes a breeze. Making C++ objects available remotely over the network or turning them into a web service is as easy as adding a few annotations to a header file. The Remoting code generator does the rest. There is no need to maintain a separate interface definition, using an awkward interface definition language.
Remoting has been developed by Applied Informatics. Like OSP, it was first released under a commercial license. For macchina.io EDGE, the core of Remoting (core library, code generator and TCP transport) has been released under an open source license. The full version of Remoting (including support for SOAP and WSDL, as well as JSON-RPC) is available from Applied Informatics under a commercial license.
In macchina.io EDGE, Remoting is used for the C++-to-JavaScript bridging mechanism. It can also be used for efficient RPC-based inter-process communication, using the TCP transport.
JavaScript Environment
The JavaScript environment in macchina.io EDGE is based on the Google V8 engine. V8 is the JavaScript engine used in the Google Chrome browser and node.js, the well-known server-side JavaScript platform.
There are bindings that allow using certain features of the POCO C++ Libraries in JavaScript code. Examples are database access (SQLite), HTTP(S) client, access to application configuration and environment, OSP service registry, etc.
A generic C++-to-JavaScript bridging mechanism makes it possible to access C++ objects from JavaScript code, without the need to manually write glue code.
IoT Components
The IoT Components are the "heart" of macchina.io EDGE. Various OSP bundles and services implement features such as interfaces to devices and sensors, network protocols such as MQTT or COAP, interfaces to cloud services (e.g., for sending SMS or Twitter messages), and the web-based user interface of macchina.io EDGE.
Devices and Sensors
macchina.io EDGE defines generic interfaces for various kinds of sensors and devices. Based on these interfaces, different implementations are available that make specific sensors and devices available in macchina.io EDGE. There are interfaces and implementations for generic sensor types such as temperature or humidity sensors, GNSS/GPS receivers, accelerometers, triggers, GPIO ports, serial port devices, etc.
Protocols
macchina.io EDGE implements various protocols for talking to sensor networks, automation systems, or cloud services. One such protocol is MQTT, a publish-subscribe based "light weight" messaging protocol for use on top of the TCP/IP protocol, which is popular for building cloud-connected IoT applications. In macchina.io EDGE, MQTT is implemented using the Eclipse Paho C library.
Note: In the first release of macchina.io EDGE, only MQTT is implemented. Future versions will implement additional protocols, such as COAP or Modbus.
Services
macchina.io EDGE implements services for publish-subscribe based communication with browser-based applications using web sockets (WebEvent), services for sending SMS and Twitter messages, which can be used from both C++ and JavaScript code.
Web User Interface
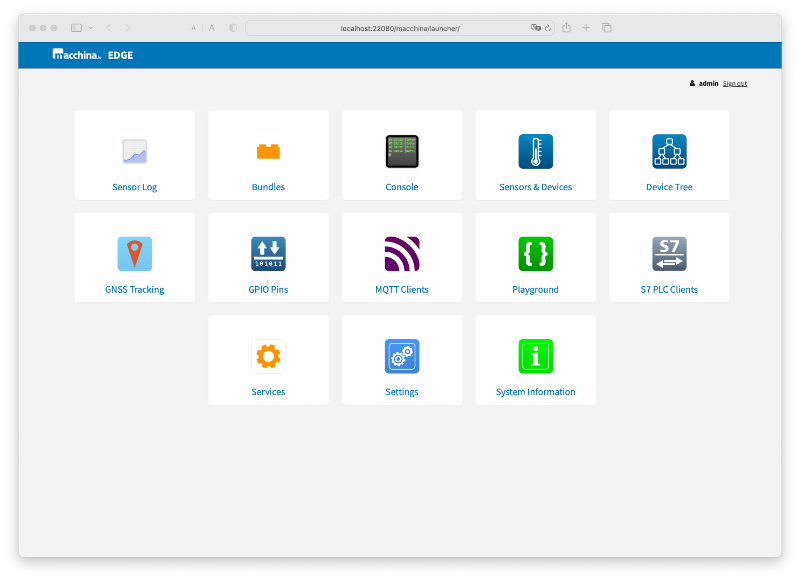
The user interface of macchina.io EDGE is entirely web-based. It is implemented using the web server built into OSP. Parts of the web interface (e.g., System Information, Sensors and Devices, GNSS Tracking, MQTT Clients) are built entirely in JavaScript, both on the client and on the server side. Other parts combine JavaScript on the client side with C++ REST services on the server side.
The web user interface mostly uses jQuery and AngularJS. It is based on the concept of "Apps". After logging in, the user sees a grid of app icons (e.g., "Bundles", "Sensors & Devices", "Playground", etc.). Clicking an icon will "launch" the respective app. New apps can be added to macchina.io EDGE simply by installing new bundles. A highlight of the web user interface is the "Playground" app. It provides a browser-based JavaScript editor and allows running JavaScript code on the macchina.io EDGE server. The "Playground" app can also be used to create a new JavaScript application bundle, which can be installed on a macchina.io EDGE device.